Use machine learning algorithm to predict whether an RNA sequence can form a circular RNA
October 04, 2016
In this problem, we are given reference genome of Homo sapiens and the genomic loci of all circRNAs. Given a certain genomic locus, our goal is to develop a classifier to predict whether a pair of two loci will form a circRNA or not
FASTA format is used to store reference genome. Details of this format can be found in (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTA_format). For python user, we use tools like biopython to parse fasta files (https://www.biostars.org/p/710/).
All other data are stored in BED format. chrom is the name of the chromosome. chromStart is the starting position of the circRNA in the chromosome. Note that the first base in a chromosome is numbered 0; chromEnd is the ending position of the circRNA in the chromosome. Note that chromEnd base should not be included in the display of circRNA. For example, the first 200 bases of a chromosome are defined as chromStart=0, chromEnd=200, and span the bases numbered 0-199. strand defines the strand that circRNA lies in. Note that the FASTA file of the reference genome only contains + strand, we should covert + strand to − strand. A complete description of BED format can be found in http://genome.ucsc.edu/FAQ/FAQformat.html#format1
hsa hg19 Rybak2015.bed stores the genomic loci of circRNAs (positions where DNA sequence can be transcribed and form circRNAs) of Homo sapiens. These data are considered as positive examples.
all exons.bed store thes genomic loci of exons. We should use this file to construct negative examples. All exons that are not overlapped with circRNAs can be considered as negative examples. hg19 Alu.bed stores the genomic loci of Alu.
Dependency package:
- Python 3.5
- Keras 1.2.0
- Tensorflow r0.12
- Numpy 1.7.1
neural network structure: 10000->640(relu)->dropout->64(relu)->dropout->1(sigmoid)
# coding:utf-8
from keras.models import Sequential
import numpy as np
import random
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import sequence
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Embedding, LSTM, Bidirectional, SimpleRNN
from keras.layers.core import Activation
dna2int = {
'A': 1,
'T': 2,
'C': 3,
'G': 4,
'a': 5,
't': 6,
'c': 7,
'g': 8,
'N': 9,
}
def dna2vec(dna):
d = []
for c in dna:
if c == '\n':
continue
temp_l = [0 for i in range(10)]
temp_l[dna2int[c]] = 1
d.append(temp_l)
return d
def dna_to_int(dna):
d = []
for c in dna:
if c == '\n':
break
d.append(dna2int[c])
return d
MAX_LEN = 5000
DATA_STEP = 20000
data1 = []
data2 = []
with open('formalization_all_exons_lines.txt', 'r') as f1:
with open('formalization_hsa_hg19_Rybak2015_lines.txt', 'r') as f2:
lines_1 = f1.readlines()
lines_2 = f2.readlines()
data_start_number_1 = random.randint(0, len(lines_1) - DATA_STEP)
data_start_number_2 = random.randint(0, len(lines_2) - DATA_STEP)
print('data_start_number_1 :', data_start_number_1, 'data_start_number_2 :', data_start_number_2)
dataX = lines_1[data_start_number_1:data_start_number_1+DATA_STEP] + lines_2[data_start_number_2:data_start_number_2+DATA_STEP]
dataY = [1 for i in range(DATA_STEP)] + [0 for i in range(DATA_STEP)]
testX = lines_1[:1000] + lines_2[:1000]
testY = [1 for i in range(1000)] + [0 for i in range(1000)]
testX = [dna_to_int(l) for l in testX]
dataX = [dna_to_int(l) for l in dataX]
dataY = dataY
data_set = dataX
test_set = testX
target_set = np.array(dataY, np.int)
test_tag_set = target_set
data_set = sequence.pad_sequences(data_set, maxlen=MAX_LEN, dtype='int32')
test_set = sequence.pad_sequences(test_set, maxlen=MAX_LEN, dtype='int32')
data_set = np.array(data_set)
test_set = np.array(test_set)
data = data_set
X_train = data_set
Y_train = target_set
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(640, input_dim=MAX_LEN))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.1))
model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=MAX_LEN))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.1))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile('adam', 'binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
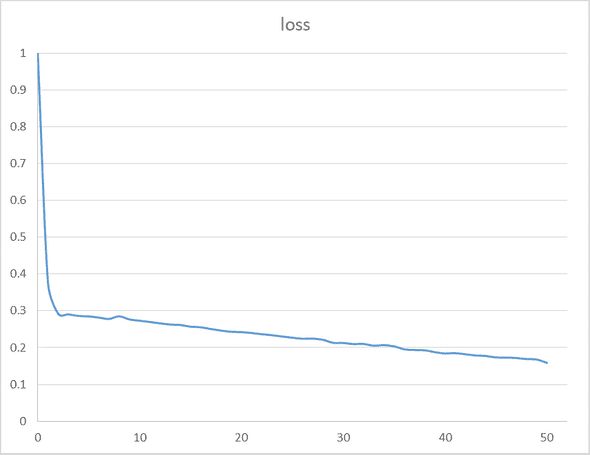
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, nb_epoch=50, batch_size=32)
print(model.evaluate(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=32))
for i in range(30):
step = 1000
start_number_1 = random.randint(0, len(lines_1) - step)
start_number_2 = random.randint(0, len(lines_2) - step)
print('start_number_1 :', start_number_1, 'start_number_2 :', start_number_2)
testX = lines_1[start_number_1:start_number_1+step] + lines_2[start_number_2:start_number_2+step]
testY = [1 for i in range(step)] + [0 for i in range(step)]
testX = [dna_to_int(l) for l in testX]
test_set = sequence.pad_sequences(testX, maxlen=MAX_LEN, dtype='int32')
test_set = np.array(test_set)
test_tag_set = np.array(testY, np.int)
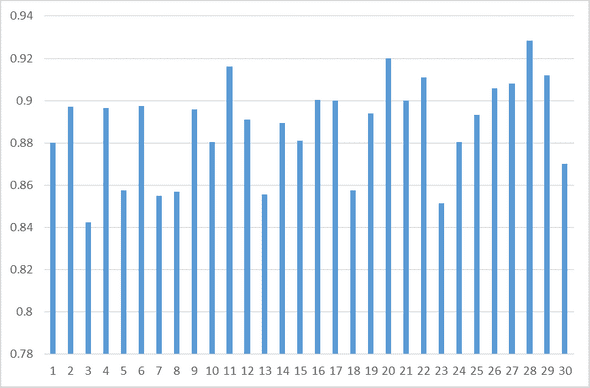
print(model.evaluate(test_set, test_tag_set, batch_size=32))- train dataset size: 40000
- accuracy: 0.94082
- total time: 55.8 minutes
test dataset(random) :
- step size : 2000
- total size : 30
- accuracy :